Jeremy Vachier
Theoretical Physicist | Associate Director Data Science
Projects
Featured Projects
Scientific Literature RAG System
AI-powered introduction generator for scientific papers
Live demonstration of the Scientific Literature RAG system generating introductions with semantic search and citation extraction.
A production-ready RAG system that automatically generates well-structured, literature-informed introductions for scientific papers. The system indexes research papers and leverages LLMs to synthesize relevant literature into comprehensive introductions with properly formatted citations.
Key Features:
- Multi-Provider LLM Support: Claude (Anthropic), OpenAI GPT-4/GPT-4o, Google Gemini
- SPECTER2 Embeddings: Domain-optimized scientific embeddings for superior semantic understanding
- GPU Acceleration: Metal GPU support for Apple Silicon, CUDA for NVIDIA, automatic CPU fallback
- Smart PDF Processing: Semantic chunking (500-word chunks with 50-word overlap)
- ChromaDB Vector Search: Persistent local storage with cosine similarity search
- Automatic BibTeX Citations: Extracts and formats references with sophisticated metadata extraction
- Interactive Dash UI: User-friendly web interface for literature exploration
- ROUGE Evaluation: Built-in evaluation metrics for assessing generation quality (F1 scores >0.5)
Performance:
- Embedding: 50-100 chunks/second on Apple Silicon
- Generation: 10-30 seconds per introduction
- Indexing: ~1 minute per 100 PDFs
Technologies: Python 3.11+, GPU, LLM, ChromaDB, SPECTER2, RAG, Dash
Status: Production Ready | Apache 2.0 License
→ View on GitHub
Speech-to-Text with Sentiment Analysis and Translation
Real-time multilingual processing pipeline
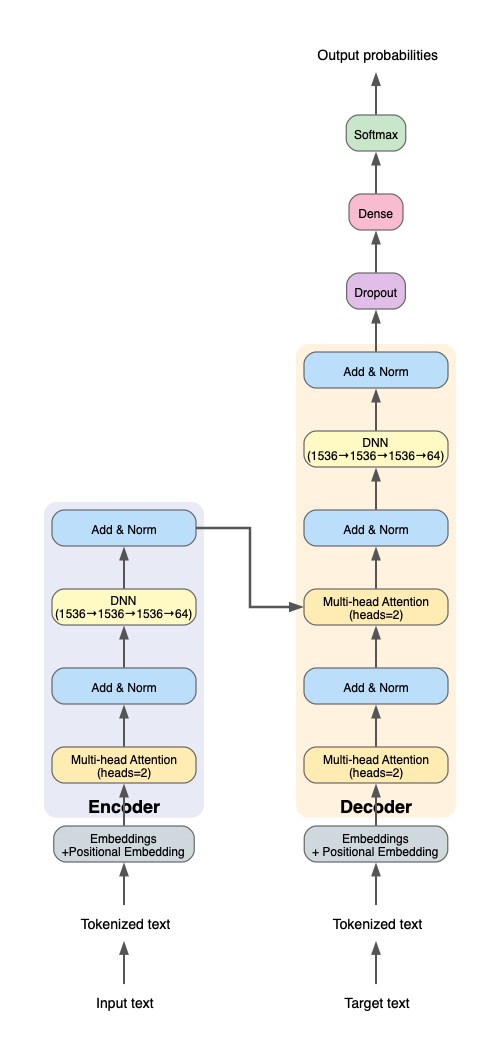
Detailed architecture of the Transformer model showing encoder-decoder structure with multi-head attention mechanisms.
A comprehensive end-to-end system integrating speech recognition, sentiment analysis, and neural machine translation. Built with from-scratch Transformer implementation demonstrating deep understanding of attention mechanisms and encoder-decoder architectures.
Key Features:
- Real-time Speech-to-Text: Audio capture and transcription using Vosk library (English)
- From-Scratch Transformer: Complete encoder-decoder architecture without pre-trained models
- Custom Multi-Head Attention: Manually implemented attention mechanisms with configurable heads
- Positional Encoding: Hand-crafted sinusoidal position embeddings
- Sentiment Classification: Bidirectional LSTM with 95% test accuracy
- Interactive Dash Web App: Real-time processing with visual feedback and export functionality
- Hyperparameter Optimization: Automated tuning with Optuna for both models
- BLEU Score Evaluation: Translation quality metrics and model assessment
Performance Metrics:
- Sentiment Analysis (BiLSTM): 95.00% test accuracy
- Translation (Transformer): 67.26% test accuracy, 0.52 BLEU score
- Real-time processing with instant speech recognition and translation
Architecture Highlights:
- Educational implementation demonstrating core concepts
- Full control over attention mechanisms and positional encodings
- Research-grade code suitable for experimentation
- Clean, well-documented implementation
Technologies: Python 3.11+, Transformer, Bidirection LSTM, TensorFlow, Keras, Vosk, Dash, Optuna
Status: Research/Educational | Apache 2.0 License
→ View on GitHub
Active Particles in 3D Confinement
GPU-accelerated molecular dynamics simulation
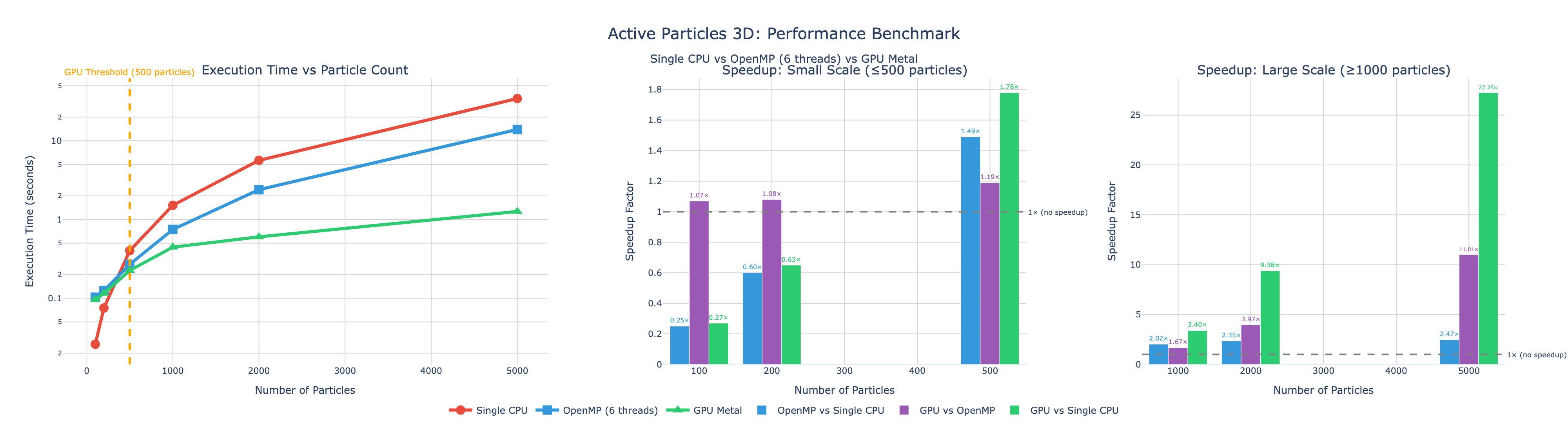
Performance comparison across CPU and GPU implementations showing up to 27× speedup on Apple Silicon.
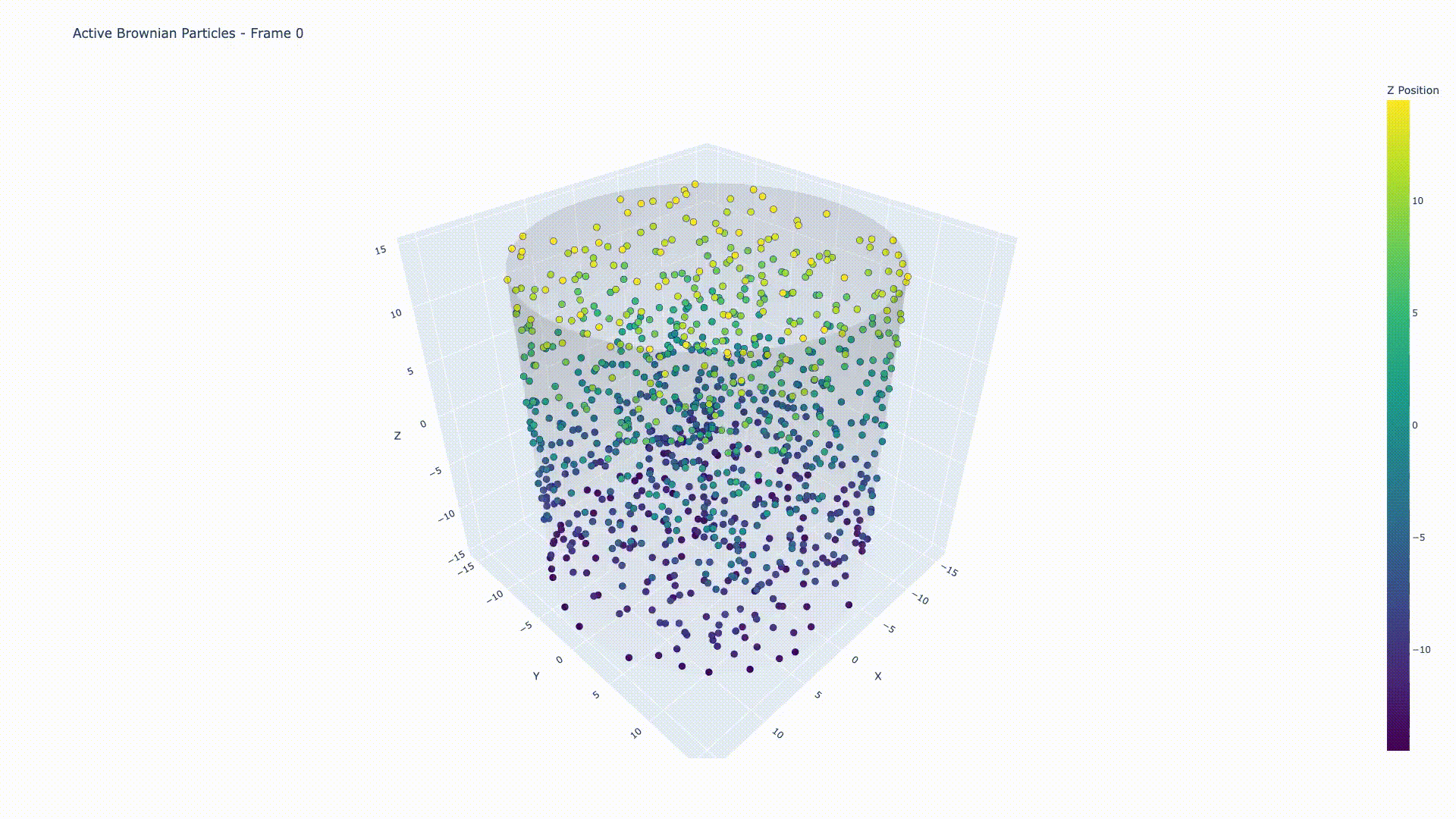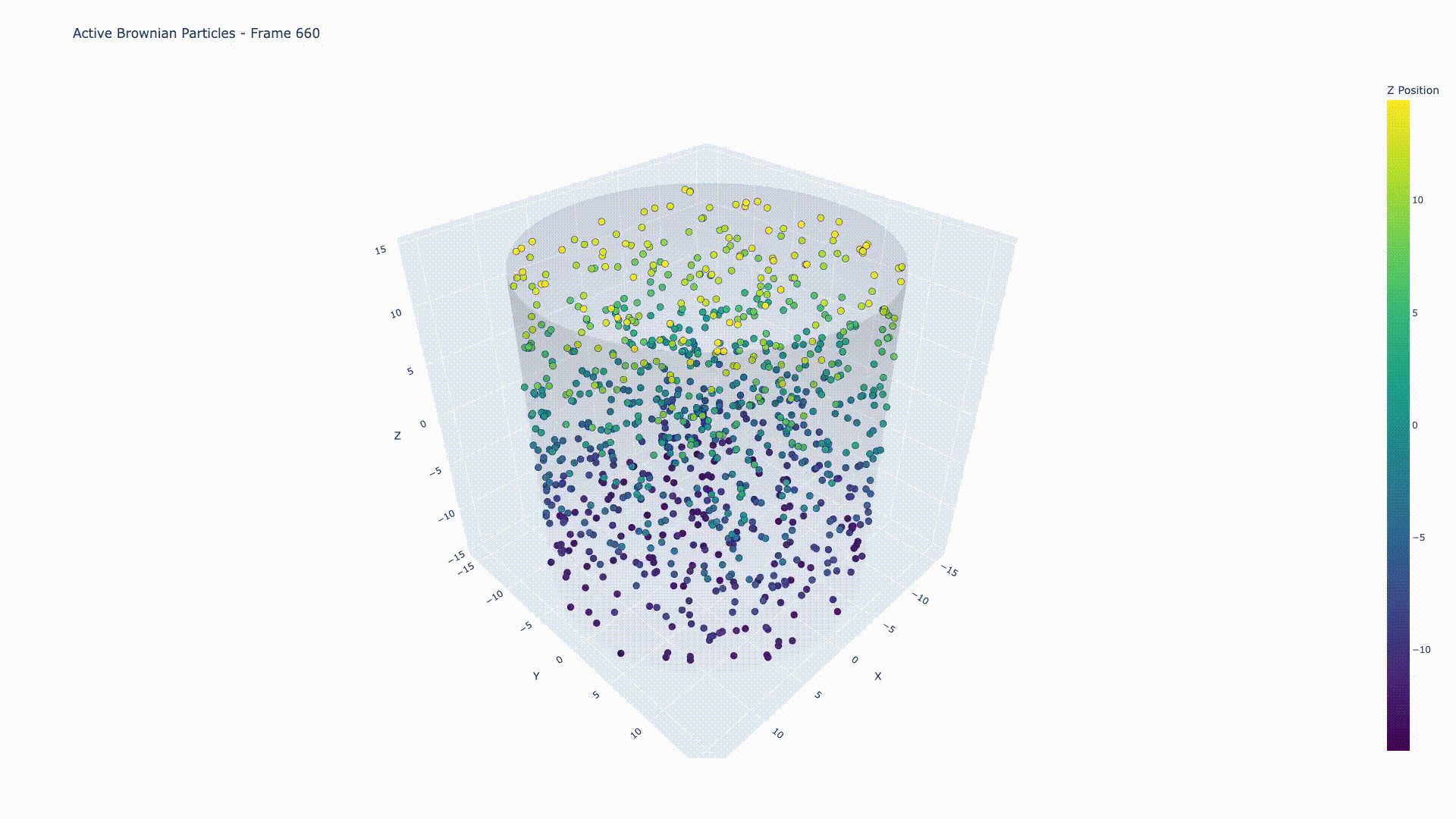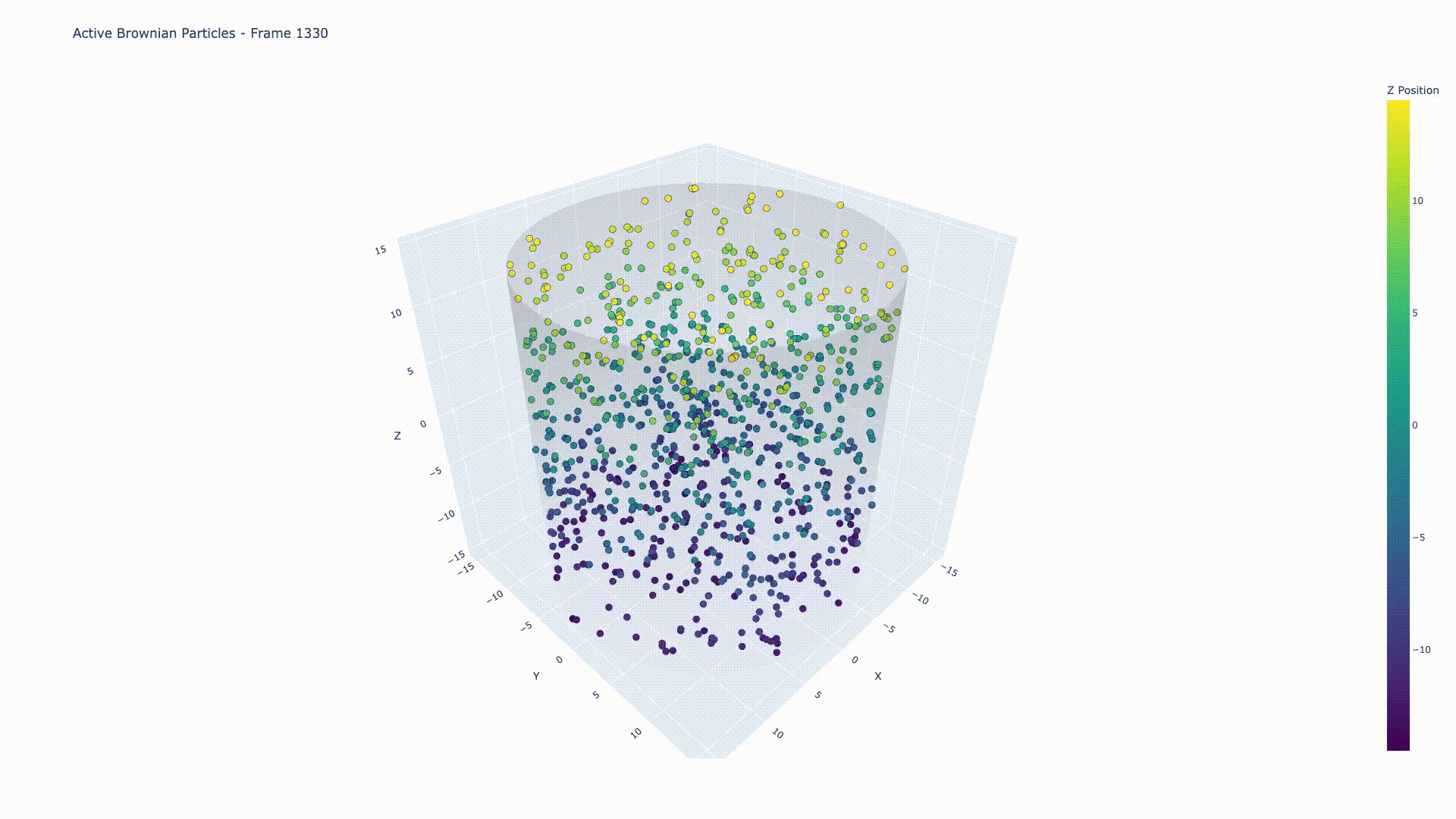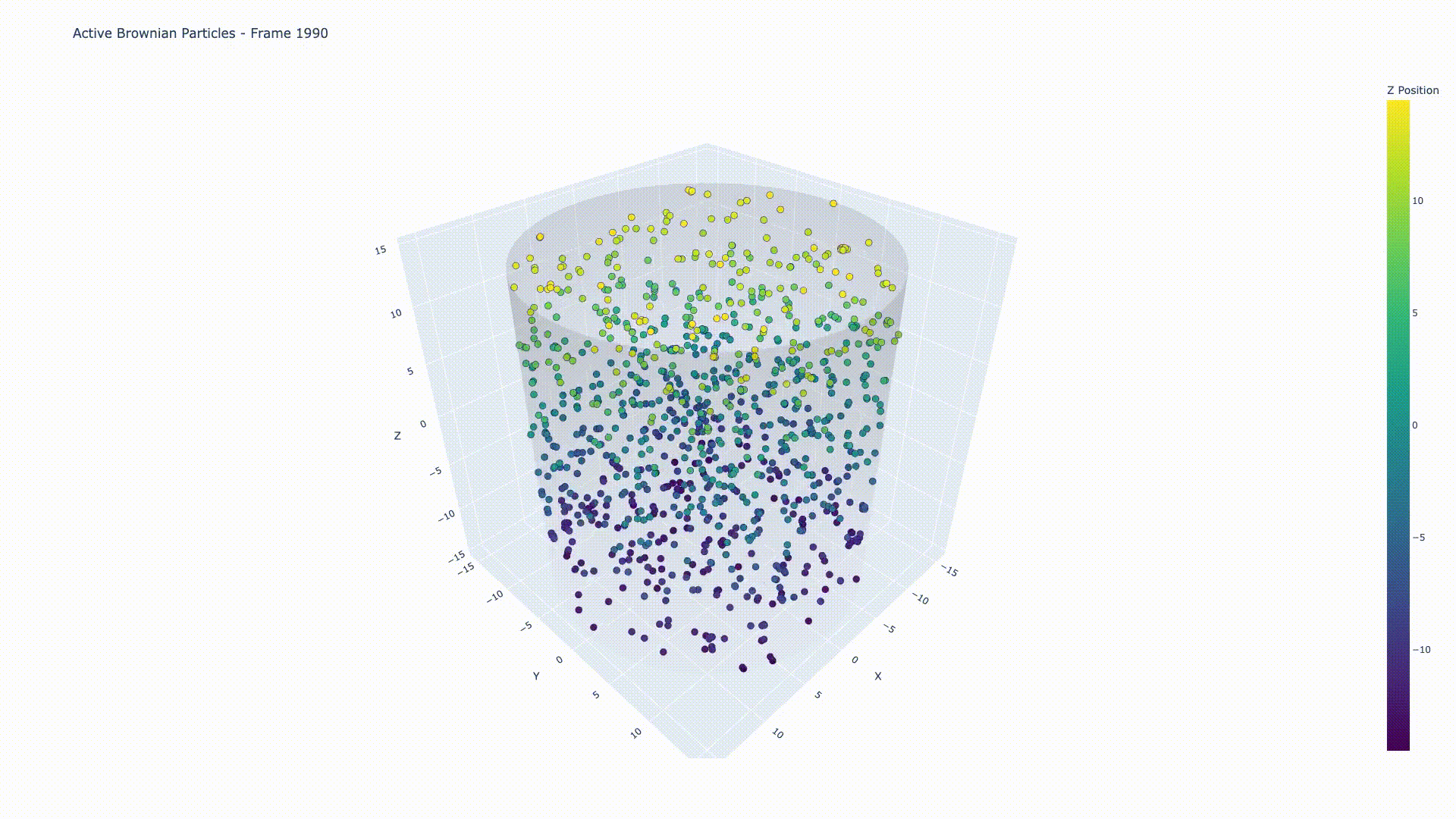
Simulation of 1000 active Brownian particles under 3D cylindrical confinement, demonstrating collective motion and particle-particle interactions with Lennard-Jones repulsion.
A high-performance C++ simulation framework for modeling active Brownian particles (ABPs) under cylindrical confinement in 3D space. Implements Euler-Maruyama algorithm for Langevin dynamics with dual CPU/GPU implementations.
Key Features:
- Dual Implementations: CPU-only (OpenMP) and GPU hybrid (Metal) versions
- GPU Acceleration: Up to 27× speedup on Apple Silicon for large systems (N ≥ 1000)
- Langevin Dynamics: Proper stochastic noise generation with Euler-Maruyama integration
- 3D Cylindrical Confinement: Reflective boundary conditions for realistic physical constraints
- Lennard-Jones Interactions: Repulsive particle-particle forces with configurable strength
- OpenMP Parallelization: Multi-threaded CPU optimization for all particle counts
- Automatic CPU/GPU Selection: Smart threshold-based switching for optimal performance
- Numerical Stability: Robust safeguards prevent NaN overflow at high particle densities
Performance Benchmarks (Apple M2, 1000 timesteps):
| Particles | CPU (1 thread) | CPU (OpenMP 6) | GPU (Metal) | GPU vs 1 CPU | GPU vs OpenMP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.026s | 0.103s | 0.096s | 0.3× | 0.9× |
| 200 | 0.075s | 0.125s | 0.115s | 0.7× | 1.1× |
| 500 | 0.401s | 0.269s | 0.225s | 1.8× | 1.2× |
| 1,000 | 1.514s | 0.747s | 0.445s | 3.4× | 1.7× |
| 2,000 | 5.638s | 2.389s | 0.601s | 9.4× | 4.0× |
| 5,000 | 34.393s | 13.903s | 1.262s | 27.3× | 11.0× |
Physical Model:
- Active Brownian particles with self-propulsion
- Translational and rotational diffusion
- Repulsive Lennard-Jones potential
- Applications: bacterial suspensions, cell motility, colloidal systems
Technologies: C++17, OpenMP, Metal GPU
Status: Research-Grade | Apache 2.0 License
→ View on GitHub
Personality Classification with Ensemble Learning
Production ML pipeline achieving Kaggle top 5%
Interactive dashboard for real-time personality classification with model explainability and performance metrics.
A production-ready machine learning pipeline for personality classification using ensemble learning, achieving top 5% (200/4,329) in the Kaggle Personality Classification Competition. Features modular architecture, automated hyperparameter optimization, and interactive visualization.
Key Features:
- Six Ensemble Stacks: Complementary ML algorithms (Random Forest, XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost, Neural Networks)
- Advanced Data Augmentation: SDV Copula-based synthetic data generation with quality control
- Automated Hyperparameter Optimization: Optuna-powered tuning for each stack (200+ trials for blending)
- Interactive Dash Dashboard: Real-time predictions, model explainability, and performance visualization
- Meta-Learning Approach: Logistic Regression ensemble combiner with optimized blending weights
- Out-of-Fold Predictions: Unbiased ensemble training with stratified cross-validation
- Production-Ready: Full test coverage, CI/CD pipeline, comprehensive logging
Ensemble Architecture:
| Stack | Focus | Algorithms | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Traditional ML (Narrow) | RF, LR, XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost | Stable baseline |
| B | Traditional ML (Wide) | Same as A | Extended search space |
| C | Gradient Boosting | XGBoost, CatBoost | Tree specialists |
| D | Sklearn Ensemble | Extra Trees, Hist GB, SVM, Gaussian NB | Diverse mix |
| E | Neural Networks | MLPClassifier, Deep architectures | Non-linear patterns |
| F | Noise-Robust | Same as A + label noise | Improved generalization |
Competition Results:
- Rank: 200/4,329 (Top 5%)
- Dataset: ~18,000+ training samples (with augmentation), 8 personality dimensions
- Cross-Validation: Stratified 5-fold CV for robust evaluation
Technologies: Python 3.11+, scikit-learn, XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost, Optuna, Dash, Plotly
Status: Production Ready | Apache 2.0 License
→ View on GitHub
Open Source Contributions
All public projects available on GitHub